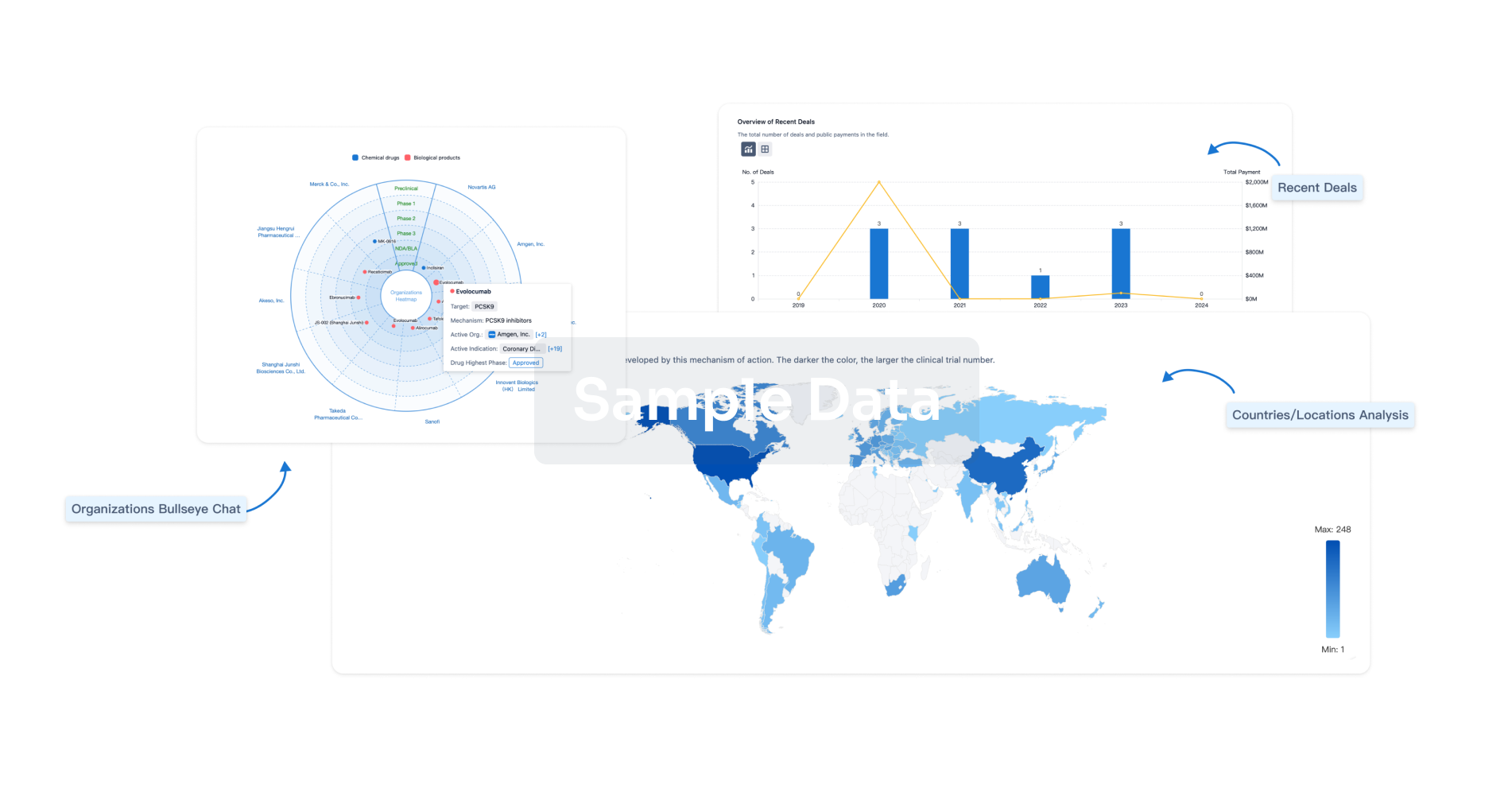
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Drug Highest Phase
Preclinical
|
First Approval Ctry. / Loc.
US
|
|
First Approval Date
31 Oct 1949
|
A Phase II Randomized Controlled Trial for the Addition of Chloroquine, an Autophagy Inhibitor, to Concurrent Chemoradiation for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma
Glioblastomas (GBM) are the most common type of primary brain tumors with an annual incidence of approximately 500 patients in the Netherlands. Despite extensive treatment including a resection, radiation therapy and chemotherapy, the median overall survival is only 14.6 months.
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) amplification or mutation is regularly observed in GBM and is thought to be a major contributor to resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The most common EGFR mutation in GBM (EGFRvIII) is present in 30-50% of GBM.
Previously MAASTRO lab has shown that expression of EGFRvIII provides GBM cells with a survival advantage when exposed to stress factors such as hypoxia and nutrient deprivation. These metabolic stress factors activate a lysosomal degradation pathway, known as autophagy. Inhibition of autophagy sensitizes cells to hypoxia, reduces the viable hypoxic fraction in tumors with > 40% and subsequently sensitizes these tumors to irradiation.
Chloroquine (CQ) is a potent autophagy blocker and is the most widely investigated substance in this context. Previously, the effect of CQ has been demonstrated in a small randomized controlled trial in GBM treated with radiotherapy and carmustine. Although not statistically significantly different, the rate of death over time was approximately half as large in patients receiving CQ as in patients receiving placebo. The intracellular effects of CQ are dose-dependent. Therefore, the authors suggest an increase in daily dose of CQ may be necessary. Furthermore, the combination of CQ with TMZ may induce more damage to the neoplastic cells.
In the phase I part of this trial the recommended dose of CQ in combination with radiotherapy and temozolomide will be tested. In the phase II part of the trial patients with a histologically confirmed GBM will be randomized between standard treatment consisting of concurrent radiotherapy with temozolomide and adjuvant temozolomide (arm A) and standard treatment plus CQ (arm B).
Monitoring Therapeutic Efficacy of Chloroquine Plus Primaquine in the Treatment of Uncomplicated Plasmodium Vivax Based on Clinical, Parasitologic and Hematologic Parameters in Shecha Health Center: Open Label Clinical Trial
The goal of this open label clinical trial will be to assess the therapeutic efficacy of chloroquine plus primaquine in the treatment of uncomplicated plasmodium vivax in Shecha Health Center, South Ethiopia.
The main question it aims to answer:- the current therapeutic efficacy of chloroquine plus primaquine in the treatment of uncomplicated plasmodium vivax in Shecha Health Center, South Ethiopia based on clinical, parasitological and hematological parameter.
Participants will be patients aged >6 months with diagnosis of plasmodium vivax mono-infection and who fulfills the inclusion criteria.
This is a single arm open label invivo therapeutic efficacy study of chloroquine plus primaquine in the treatment of uncomplicated plasmodium vivax. The final result will be compared with World Health Organization recommendation on antimalarial drug therapeutic efficacy.
100
Clinical Results associated with Hemozoin x DNA
100
Translational Medicine associated with Hemozoin x DNA
0
Patents (Medical) associated with Hemozoin x DNA