# 配置加速
curl -sSL https://get.daocloud.io/daotools/set_mirror.sh | sh -s http://f1361db2.m.daocloud.io
# 重启 Docker
systemctl restart docker
二、启用 API
为了保证安全,Docker 安装后默认不会启用远程 API 服务,因为这个服务默认不做权限认证。本文主要是做实践分享,且用于内网生产环境,安全上会有保证,如果是外网生产环境建议做好 iptables 安全加固或用完即焚或使用
TLS 安全认证
,此处不表。
开启方法比较简单,此处只分享 CentOS 7 系统的启用步骤:
1、修改配置:
vi /lib/systemd/system/docker.service
找到 ExecStart 配置项,默认如下:
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
在其中插入监听选项:-H tcp://0.0.0.0:2375(如果是内网生产环境,请将 0.0.0.0 改为内网 IP),最后为:
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// -H tcp://0.0.0.0:2375 --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
2、重启 Docker:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker
3、查看结果,如下即为成功:
[root@centos ~]# netstat -nutlp | grep 2375
tcp6 0 0 :::2375 :::* LISTEN 3586/dockerd
4、查看 API 版本:
[root@centos ~]# docker version
Client: Docker Engine - Community
Version: 19.03.2
API version: 1.40 # 本机 Docker 作为客户端的版本
Go version: go1.12.8
Git commit: 6a30dfc
Built: Thu Aug 29 05:28:55 2019
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
Server: Docker Engine - Community
Engine:
Version: 19.03.2
API version: 1.40 (minimum version 1.12) # 本机 Docker 作为服务端的版本
Go version: go1.12.8
Git commit: 6a30dfc
Built: Thu Aug 29 05:27:34 2019
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
containerd:
Version: 1.2.6
GitCommit: 894b81a4b802e4eb2a91d1ce216b8817763c29fb
runc:
Version: 1.0.0-rc8
GitCommit: 425e105d5a03fabd737a126ad93d62a9eeede87f
docker-init:
Version: 0.18.0
GitCommit: fec3683
三、Docker API 初探
完成上述步骤后,Docker 就已经支持远程控制了,我们先参考
官方文档
试试拉起一个镜像(下文的操作均在本地完成,因此 IP 均为 127.0.0.1):
1、调用 API 拉取 centos 最新镜像:
curl -XPOST "http://127.0.0.1:2375/v1.40/images/create?fromImage=centos&tag=latest"
2、调用 API 创建一个容器,指定一个前台阻塞命令 tail -f /dev/null:
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://127.0.0.1:2375/containers/create?name=demo1 -d '{
"Image": "centos:latest",
"HostConfig": {
"NetworkMode": "host",
"Binds": [
"/tmp:/tmp"
"Cmd": [
"tail","-f","/dev/null"
成功返回如下:
{"Id":"b88c7c986ecd5fdf174f79b00e024087b47241cd40653bcb05df70fba5cc398f","Warnings":[]}3、调用 API 启动刚刚创建的容器:
# 可以使用上一步返回的 id 来启动:
curl -XPOST http://127.0.0.1:2375/containers/b88c7c986ecd5fdf174f79b00e024087b47241cd40653bcb05df70fba5cc398f/start
# 也可以使用上一步定义的容器名称 demo1 来启动:
curl -XPOST http://127.0.0.1:2375/demo1/start4、查看启动中的容器:
[root@centos ~]# docker ps | grep demo1
ed9f2150f8d5 centos:latest "tail -f /dev/null" About a minute ago Up About a minute demo15、调用容器执行命令:
调用 API,对已存在的容器 demo1 创建命令实例:
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://127.0.0.1:2375/containers/demo1/exec -d '{ "AttachStdin": false,
"AttachStdout": true,
"AttachStderr": true,
"DetachKeys": "ctrl-p,ctrl-q",
"Tty": false,
"Cmd": [
"sh","-c","date | tee /tmp/test_exec.log"
"Env": [
"FOO=bar",
"BAZ=quux"
返回结果为命令实例 Id:
{"Id":"08552937782f6c5b696454d5524b140337fb0652d5f39142ac57ceaf46732bb4"}继续调用 API 启动这个命令实例:
curl -XPOST -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://127.0.0.1:2375/exec/08552937782f6c5b696454d5524b140337fb0652d5f39142ac57ceaf46732bb4/start -d '{
"Detach": false,
"Tty": false
Fri Oct 4 03:21:36 UTC 2019如上返回了一个 date 命令的回显,并且会在挂载的/tmp 目录生成 test_exec.log 文本,内容和上一步回显一致:
[root@centos ~]# cat /tmp/test_exec.log
Fri Oct 4 03:21:36 UTC 2019说明命令被成功执行!
上述步骤,简单的展示了 Docker API 的常见场景,可以说 Docker API 极大的简化了运维工作,比如我们常说的 CI/CD 就可以不再依赖 ssh 通道或自建 agent 了,一个接口就可以搞定应用的全生命周期,简直是运维大救星!
Ps:更多 Docker API 的用法可以参考官方文档 。
# -- coding: utf8 --
import docker
# 初始化,这里可以根据目标 docker 版本执行 API 版本,如果后面报错则需要调整此处为目标的同版本或更低版本
client = docker.DockerClient(version='1.40', base_url='tcp://127.0.0.1:2375')
# 拉取镜像
client.images.pull('centos:latest')
# 拉起容器
client.containers.run(image='centos:latest', name='demo1', command='tail -f /dev/null',volumes={'/data': {'bind': '/tmp', 'mode': 'rw'}}, detach=True)
# 先通过容器名获取对象
container = client.containers.get('demo1')
# 通过对象执行命令
result = container.exec_run(cmd='sh -c "date | tee /tmp/test_sdk.log"', detach=False, tty=True, stdin=True, stdout=True)
# 输出执行命令的返回码和返回结果
print(result.exit_code)
print(result.output.decode())上述代码保存为 test_sdk.py,执行 python test_sdk.py 后查看结果:
[root@centos ~]# python test_sdk.py
Sun Oct 6 01:48:58 UTC 2019
[root@centos ~]# cat /data/test_sdk.log
Fri Oct 4 03:35:14 UTC 2019通过 SDK 的操作演示,可以很明显的看到操作步骤极大的简化了,整体过程变得更加流畅!
Ps:更多的玩法可以参考官方文档 。
stats auth admin:123456
stats admin if TRUE
################################################## status end ###############################################
# 请求测试,有上述内容即为成功
curl http://127.0.0.1/127.0.0.13、制作 Haproxy 镜像:
这里直接基于官方的镜像,额外集成用于更新 Haproxy 配置的脚本以及一些常用命令(curl、vim、ps):
Dockerfile 内容如下:
FROM haproxy:latest
RUN apt-get update \
&& apt-get install -y curl vim procps \
&& apt-get purge -y --auto-remove -o APT::AutoRemove::RecommendsImportant=false
COPY update_cfg.sh /opt/
COPY docker-entrypoint.sh /
CMD ["haproxy","-f","/etc/haproxy.cfg"]update_cfg.sh 用于下载、比对、更新 Haproxy 配置,语法、逻辑都比较简单,感兴趣的可以看看:
#!/bin/bash
source /etc/profile
if [ -z $VIP ];then
echo 'ENV ${VIP} is not SET, Plz check!'
exit 1
# Define and create storage directory
etc_dir=${STORAGE_DIR:-/usr/local/haproxy/etc}
temp_dir=${etc_dir}/temp
back_dir=${etc_dir}/backup
mkdir -p ${back_dir} ${temp_dir}
# Define the configration file
current_cfg=${etc_dir}/${VIP}.cfg
backup_cfg=${back_dir}/${VIP}_$(date +%F-%H%M%S).cfg
temp_cfg=${temp_dir}/${VIP}.cfg
# Define file download configration
curl_bin=$(which curl)
cfg_manage_api=${CFG_GET_URL:-http://your_haporxy_download_svr/haproxy/}${VIP} # 这里需要根据配置管理服务的实际情况修改地址
# console log
report_log()
echo "[$(date '+%F %H:%M:%S')] $*"
# backup current configration file
backup_cfg()
if [ -f ${current_cfg} ];then
cp -a ${current_cfg} ${backup_cfg} && \
report_log "Backup ${current_cfg} to ${backup_cfg} success." || \
report_log "Backup ${current_cfg} to ${backup_cfg} failed."
report_log "${current_cfg} is not exist, maybe the first release, skiped."
# update current configration file
cover_cfg()
{ if [ -f ${temp_cfg} ];then
cp -a ${temp_cfg} ${current_cfg} && \
report_log "Cover ${temp_cfg} to ${current_cfg} success." || (
report_log "Cover ${temp_cfg} to ${current_cfg} failed."
exit 1
report_log "${temp_cfg} is not exist, Unknow Error, exited."
exit 1
# download latest configration file from download svr
download_cfg()
report_log "Starting Download configration file to ${temp_cfg} ..."
ret_code=$(${curl_bin} -s --max-time 120 --retry 3 -w %{http_code} -o ${temp_cfg} ${cfg_manage_api})
if [ $ret_code -eq 200 ] && [ $? -eq 0 ];then
report_log "Download configration file ${temp_cfg} success."
report_log "Download configration file ${temp_cfg} failed."
exit 1
# check the latest configration
check_cfg()
old_md5=$(test -f ${current_cfg} && md5sum ${current_cfg} | awk '{print $1}' 2>/dev/null )
new_md5=$(md5sum ${temp_cfg}|awk '{print $1}')
if [ "$old_md5" = "$new_md5" ];then
report_log "The configuration file ${VIP}.cfg is the same, no need update."
return 2
if haproxy -c -W -f ${temp_cfg} >/dev/null ;then
report_log "Configuration file ${temp_cfg} is valid."
return 0
report_log "Configuration file ${temp_cfg} is invalid."
return 1
download_cfg
if check_cfg;then
backup_cfg
cover_cfg && \
report_log "${current_cfg} is updated success!"
exit $?
docker-entrypoint.sh 改自 Haproxy 官方镜像,在默认逻辑块加入了对 VIP 环境变量的判断、配置文件的更新下载、配置文件软链接建立、配置语法校验等逻辑:
#!/bin/sh
# first arg is `-f` or `--some-option`
if [ "${1#-}" != "$1" ]; then
set -- haproxy "$@"
if [ "$1" = 'haproxy' ]; then
if [ -z $VIP ];then
echo echo "[$(date '+%F %H:%M:%S')] ENV \${VIP} is not SET, Plz check!"
exit 1
bash /opt/update_cfg.sh
ln -sf /usr/local/haproxy/etc/${VIP}.cfg /etc/haproxy.cfg
haproxy -W -c -f /etc/haproxy.cfg || (
echo "[$(date '+%F %H:%M:%S')] Haproxy Configuration file check failed, Plz check!"
exit 1
shift # "haproxy"
# if the user wants "haproxy", let's add a couple useful flags
# -W -- "master-worker mode" (similar to the old "haproxy-systemd-wrapper"; allows for reload via "SIGUSR2")
# -db -- disables background mode
set -- haproxy -W -db "$@"
exec "$@"准备好上述文件后,在文件同级目录执行如下命令构建 Haproxy 镜像(实际这一步也可以通过 API 来操作,这里不再赘述,详见官方文档 ):
# 脚本给执行权限:
chmod +x *.sh
# 如果有私有仓库的可以撸到私有仓库,本文主要是分享,这里直接本地构建:
docker build -t "haproxy-plus:latest" ./4、拉起 Haproxy 容器
为了贴合文章主题,所以这里继续用 Docker API 远程方式拉起容器:
# -- coding: utf8 --
import docker
client = docker.DockerClient(version='1.40', base_url='tcp://127.0.0.1:2375')
#client.images.pull('haproxy-plus:latest') # 本地测试,所以这里不需要拉取镜像
client.containers.run(image='haproxy-plus:latest', name='demo2', volumes={'/data/images/haproxy/etc': {
'bind': '/usr/local/haproxy/etc', 'mode': 'rw'}}, network_mode='host', environment=["VIP=127.0.0.1", "CFG_GET_URL=http://127.0.0.1/"], detach=True)几个关键的设置说明:
挂载本地目录 /data/images/haproxy/etc 到容器 /usr/local/haproxy/etc 目录,用于持久化配置; 环境变量 VIP,用于指定 haproxy 的配置名称(在我们这边其实就是 VIP 地址),也是为了通过接口拉取到指定配置; 环境变量 CFG_GET_URL,拉取 Haproxy 配置的地址,组合 VIP 后就是 http://127.0.0.1/127.0.01,即上文的临时搭建的下载地址 上述 Python 代码保存为 start.py,执行结果如下:
[root@centos haproxy]# python start.py
[root@centos haproxy]# docker logs -f demo2 # 查看执行日志
[2019-10-04 04:32:10] Starting Download configration file to /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg ...
[2019-10-04 04:32:10] Download configration file /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg success.
[2019-10-04 04:32:10] Configuration file /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg is valid.
[2019-10-04 04:32:10] /usr/local/haproxy/etc/127.0.0.1.cfg is not exist, maybe the first release, skiped.
[2019-10-04 04:32:10] Cover /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg to /usr/local/haproxy/etc/127.0.0.1.cfg success.
[2019-10-04 04:32:10] /usr/local/haproxy/etc/127.0.0.1.cfg is updated success!
Configuration file is valid
[NOTICE] 276/043210 (1) : New worker #1 (27) forked通过 Docker 的日志,启动过程解析如下:
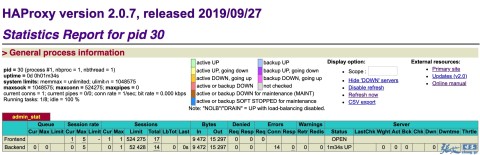
通过接口下载 Haproxy 配置,保存为 /usr/local/haporxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg; 执行 Haproxy 配置语法校验:haproxy -c -W /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg; 语法校验成功后,通过 MD5 值来比对配置是否有更新,发现找不到原来的配置,说明是首次启动; 拷贝临时配置文件到正式配置文件:/usr/local/haproxy/etc/127.0.0.1.cfg 启动 Haproxy 成功:New worker #1 (27) forked 此时,访问配置 haproxy 状态页面 http://<IP>:8080/haproxy,输入账号密码:admin/123456 看看效果:
Haproxy 状态页 结果符合预期,下面我们来尝试更新配置,更新脚本编写如下,对 Docker API 的 SDK 稍微做了下封装:
# -- coding: utf8 --
import docker
class dockerApi():
def __init__(self,ip,port=2375):
self.base_url = 'tcp://%s:%s' % (ip,port)
self.client = docker.DockerClient(
version='1.40', base_url=self.base_url)
def exec_cmd(self,container_name, cmd='echo ok',decode=True):
container = self.client.containers.get(container_name)
result = container.exec_run(
cmd=cmd, detach=False, tty=True, stdin=True, stdout=True)
ret_code = result.exit_code
if decode:
ret_info = result.output.decode()
else:
ret_info = result.output
return ret_code, ret_info
def send_kill(self, container_name):
container = self.client.containers.get(container_name)
container.kill('SIGUSR2')
# 定义 haproxy 宿主机 IP,可以是多个
ld_list = ['127.0.0.1']
# 定义更新配置的命令
cmd = 'bash /opt/update_cfg.sh'
# 定义容器名称
container_name = 'demo2'
# 开始更新
for i in ld_list:
obj = dockerApi(i)
ret_code,ret_info = obj.exec_cmd(container_name, cmd)
print '%s exec %s ret_code is: %s, exec ret_info:' % (i, cmd, ret_code)
print ret_info
if int(ret_code) == 0:
obj.send_kill(container_name)保存为 update.py,执行结果如下:
[root@centos haproxy]# python update.py
127.0.0.1 exec bash /opt/update_cfg.sh ret_code is: 2, exec ret_info:
[2019-10-04 04:55:41] Starting Download configration file to /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg ...
[2019-10-04 04:55:41] Download configration file /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg success.
[2019-10-04 04:55:41] The configuration file 127.0.0.1.cfg is the same, no need update.日志提示为,配置没有变化,所以不需要升级,符合预期。下面,我们修改中心配置,将监听的端口从 8080 改为 8181:
cat > /usr/share/nginx/html/127.0.0.1 <<EOF
global
nbproc 1
pidfile /usr/local/haproxy/logs/127.0.0.1.pid
defaults
timeout connect 300s
timeout client 300s
timeout server 300s
listen admin_stat_8181
bind 0.0.0.0:8181
mode http
stats refresh 60s
stats uri /haproxy
stats auth admin:123456
stats admin if TRUE
################################################## status end ###############################################
# 请求测试,有上述内容即为成功
curl http://127.0.0.1/127.0.0.1再次执行结果如下:
[root@centos haproxy]# python update.py
127.0.0.1 exec bash /opt/update_cfg.sh ret_code is: 0, exec ret_info:
[2019-10-04 05:03:43] Starting Download configration file to /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg ...
[2019-10-04 05:03:43] Download configration file /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg success.
[2019-10-04 05:03:43] Configuration file /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg is valid.
[2019-10-04 05:03:43] Backup /usr/local/haproxy/etc/127.0.0.1.cfg to /usr/local/haproxy/etc/backup/127.0.0.1_2019-10-04-050343.cfg success.
[2019-10-04 05:03:43] Cover /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg to /usr/local/haproxy/etc/127.0.0.1.cfg success.
[2019-10-04 05:03:43] /usr/local/haproxy/etc/127.0.0.1.cfg is updated success!相比首次启动的日志,更新配置的过程如下:
通过接口下载 Haproxy 配置,保存为 /usr/local/haporxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg; 执行 Haproxy 配置语法校验:haproxy -c -W /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg; 语法校验成功后,通过 MD5 值来比对配置是否有更新,如果有更新,先备份原配置文件到 /usr/local/haproxy/etc/backup/127.0.0.1_2019-10-04-050343.cfg; 拷贝临时配置文件到正式配置文件:/usr/local/haproxy/etc/127.0.0.1.cfg 由于容器里面的 update_cfg.sh 脚本仅更新配置文件,因此 Python 脚本最后一步还会校验脚本返回码,如果是符合预期的将会发送一个 kill 指令,平滑重载 Haproxy,这里主要是用到的 Haproxy 的-W 参数,官方解释 如下:
If you used a bind mount for the config and have edited your haproxy.cfg file, you can use HAProxy's graceful reload feature by sending a SIGHUP to the container:
$ docker kill -s HUP my-running-haproxy
The entrypoint script in the image checks for running the command haproxy and replaces it with haproxy-systemd-wrapper from HAProxy upstream which takes care of signal handling to do the graceful reload. Under the hood this uses the -sf option of haproxy so "there are two small windows of a few milliseconds each where it is possible that a few connection failures will be noticed during high loads" (see Stopping and restarting HAProxy ). Image Variants
继续查看容器的日志,可以看到有 2 段日志,第一段是首次启动,第二段则是更新配置后,发送 kill 指令,Haproxy 重载的日志:
[root@centos haproxy]# docker logs -f demo2
[2019-10-04 05:03:19] Starting Download configration file to /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg ...
[2019-10-04 05:03:20] Download configration file /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg success.
[2019-10-04 05:03:20] Configuration file /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg is valid.
[2019-10-04 05:03:20] /usr/local/haproxy/etc/127.0.0.1.cfg is not exist, maybe the first release, skiped.
[2019-10-04 05:03:20] Cover /usr/local/haproxy/etc/temp/127.0.0.1.cfg to /usr/local/haproxy/etc/127.0.0.1.cfg success.
[2019-10-04 05:03:20] /usr/local/haproxy/etc/127.0.0.1.cfg is updated success!
Configuration file is valid
[NOTICE] 276/050320 (1) : New worker #1 (27) forked
[WARNING] 276/050343 (1) : Reexecuting Master process
[NOTICE] 276/050343 (1) : New worker #1 (53) forked
[WARNING] 276/050343 (27) : Stopping proxy admin_stat in 0 ms.
[WARNING] 276/050343 (27) : Stopping frontend GLOBAL in 0 ms.
[WARNING] 276/050343 (27) : Proxy admin_stat stopped (FE: 0 conns, BE: 0 conns).
[WARNING] 276/050343 (27) : Proxy GLOBAL stopped (FE: 0 conns, BE: 0 conns).
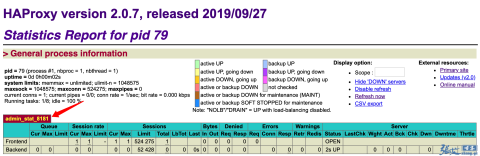
[WARNING] 276/050343 (1) : Former worker #1 (27) exited with code 0 (Exit)最后,再次访问 Haporxy 的状态页面 http://<IP>:8181/haproxy 验证效果,端口已成功更新为 8181,符合预期:
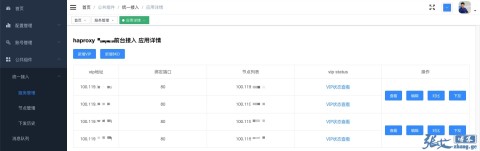
Haproxy 状态页 上述更新配置、重载的过程经过我实测,确认是平滑无损的。在生产环境,我们只需要在运维平台集中管理 Haproxy 的配置,就可以通过 Docker 的 API 来控制 Haproxy 进行秒级配置更新了!是不是相当给力?
Haproxy 运维管理 这里顺便分享一个好消息:Haproxy 最新的 2.0 已经支持 Dataplaneapi 来远程管理配置了,感兴趣的可以看下官方文档 。
本文从 Docker 安装、Docker Remote API 以及 Python SDK 的使用,较为详细的展示了 Docker Remote API 的常用场景,最后基于 Docker Remote API 分享了一个可快速落地的 Haproxy 远程管理最佳实践,希望对有需要的朋友有所帮助。
下面这步怎么搞?执行tail -f /dev/null 命令行就卡住了啊,接着的代码和返回是怎么回事?
用API创建一个容器,指定一个前台阻塞命令 tail -f /dev/null:
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://127.0.0.1:2375/containers/create?name=demo1 -d '{
"Image": "centos:latest",
"HostConfig": {
"NetworkMode": "host",
"Binds": [
"/tmp:/tmp"
"Cmd": [
"tail","-f","/dev/null"