### 2.1.1 远程过程调用 (RPC)
Remote Procedure Calls 远程过程调用 (RPC) 是一种协议,就是从一台机器(客户端)上通过参数传递的方式调用另一台机器(服务器)上的一个函数或方法(可以统称为服务)并得到返回的结果。
通常的实现有 **XML-RPC , JSON-RPC ,** 通信方式基本相同, 所不同的只是传输数据的格式。
RPC是分布式架构的核心,按响应方式分如下两种:
**同步调用:** 客户端调用服务方方法,等待直到服务方返回结果或者超时,再继续自己的操作;
**异步调用:** 客户端把消息发送给中间件,不再等待服务端返回,直接继续自己的操作;
同步调用的实现方式有WebService和RMI。
Web Service提供的服务是基于web容器的,底层使用http协议,因而适合不同语言异构系统间的调用。
RMI(Remote Method Invocation,远程方法调用)实际上是Java语言的RPC实现,允许方法返回 Java 对象以及基本数据类型,适合用于JAVA语言构建的不同系统间的调用。
异步调用的JAVA实现版就是JMS(Java Message Service),目前开源的的JMS中间件有Apache社区的ActiveMQ、Kafka消息中间件,另外有阿里的RocketMQ。
### 2.1.2 RPC框架
一个完整的RPC架构里面包含了四个核心的组件,分别是Client,Client Stub,Server以及Server Stub,这个Stub可以理解为存根。
* 客户端(Client),服务的调用方。
* 客户端存根(Client Stub),存放服务端的地址消息,再将客户端的请求参数打包成网络消息,然后通过网络远程发送给服务方。
* 服务端(Server),真正的服务提供者。
* 服务端存根(Server Stub),接收客户端发送过来的消息,将消息解包,并调用本地的方法。
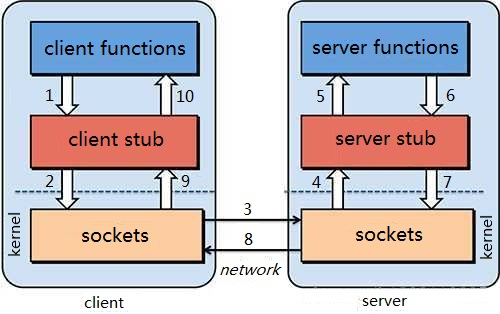
### 2.1.3 RPC调用流程
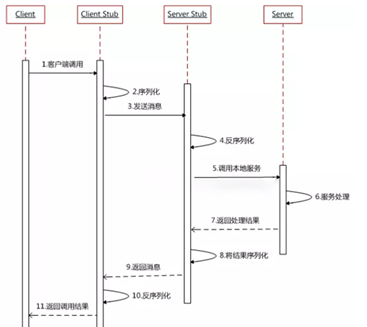
**具体实现步骤:**
1、 服务调用方(client)(客户端)以本地调用方式调用服务;
2、 client stub接收到调用后负责将方法、参数等组装成能够进行网络传输的消息体;在Java里就是序列化的过程;
3、 client stub找到服务地址,并将消息通过网络发送到服务端;
4、 server stub收到消息后进行解码,在Java里就是反序列化的过程;
5、 server stub根据解码结果调用本地的服务;
6、 本地服务执行处理逻辑;
7、 本地服务将结果返回给server stub;
8、 server stub将返回结果打包成消息,Java里的序列化;
9、 server stub将打包后的消息通过网络并发送至消费方;
10、 client stub接收到消息,并进行解码, Java里的反序列化;
11、 服务调用方(client)得到最终结果。
RPC框架的目标就是把2-10步封装起来,把调用、编码/解码的过程封装起来,让用户像调用本地服务一样的调用远程服务。要做到对客户端(调用方)透明化服务, RPC框架需要考虑解决如下问题:
**1、通讯问题** : 主要是通过在客户端和服务器之间建立TCP连接,远程过程调用的所有交换的数据都在这个连接里传输。连接可以是按需连接,调用结束后就断掉,也可以是长连接,多个远程过程调用共享同一个连接。
**2、寻址问题** : A服务器上的应用怎么告诉底层的RPC框架,如何连接到B服务器(如主机或IP地址)以及特定的端口,方法的名称是什么,这样才能完成调用。比如基于Web服务协议栈的RPC,就要提供一个endpoint URI,或者是从UDDI服务上查找。如果是RMI调用的话,还需要一个RMI Registry来注册服务的地址。
**3、序列化与反序列化** : 当A服务器上的应用发起远程过程调用时,方法的参数需要通过底层的网络协议如TCP传递到B服务器,由于网络协议是基于二进制的,内存中的参数的值要序列化成二进制的形式,也就是序列化(Serialize)或编组(marshal),通过寻址和传输将序列化的二进制发送给B服务器。
同理,B服务器接收参数要将参数反序列化。B服务器应用调用自己的方法处理后返回的结果也要序列化给A服务器,A服务器接收也要经过反序列化的过程。
## 2.2 以太坊RPC实现
JSON-RPC是区块链外部调用的标配了。以太坊同样也实现了这个功能。底层支持四种协议:InProc,IPC,HTTP,WEBSOCKED。上层除了常规的方法调用之外还实现了Pub/Sub功能。本文主要分析以太坊是如何支持这些个功能的。
### 2.2.1 api发布
api接口分布在各个模块,主要分为两种
* 1:直接code在Node中的几个service(admin,web3j,debug etc)
* 2: 实现了Service接口的服务结构,已经注册的服务会调用APIs()方法获得其中的api。
//file go-ethereum/node/node.go
func (n *Node) startRPC(services map[reflect.Type]Service) error {
apis := n.apis()
for _, service := range services {
apis = append(apis, service.APIs()...)
node中写死的接口
// node中写死的接口
func (n *Node) apis() []rpc.API {
return []rpc.API{
Namespace: "admin",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateAdminAPI(n),
Namespace: "admin",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicAdminAPI(n),
Public: true,
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: debug.Handler,
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicDebugAPI(n),
Public: true,
Namespace: "web3",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicWeb3API(n),
Public: true,
Ethereum 服务实现的APIs()接口 类似的还有其他的服务(dashboard,ethstats)
//Ethereum 服务实现的APIs()接口
func (s *Ethereum) APIs() []rpc.API {
apis := ethapi.GetAPIs(s.ApiBackend)
// Append any APIs exposed explicitly by the consensus engine
apis = append(apis, s.engine.APIs(s.BlockChain())...)
// Append all the local APIs and return
return append(apis, []rpc.API{
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicEthereumAPI(s),
Public: true,
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicMinerAPI(s),
Public: true,
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: downloader.NewPublicDownloaderAPI(s.protocolManager.downloader, s.eventMux),
Public: true,
Namespace: "miner",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateMinerAPI(s),
Public: false,
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: filters.NewPublicFilterAPI(s.ApiBackend, false),
Public: true,
Namespace: "admin",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateAdminAPI(s),
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicDebugAPI(s),
Public: true,
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateDebugAPI(s.chainConfig, s),
Namespace: "net",
Version: "1.0",
Service: s.netRPCService,
Public: true,
}...)
这里的Service只是类型,还要注册到Server里面,原理就是反射出结构体里的类型,解析出函数方法名称(转小写),参数名称,返回类型等信息,最终每个合格的方法都会生成service实例。
type service struct {
name string // name for service
typ reflect.Type // receiver type
callbacks callbacks // registered handlers
subscriptions subscriptions // available subscriptions/notifications
//反射除Service Api的结构方法
//file go-ethereum/rpc/utils.go
func suitableCallbacks(rcvr reflect.Value, typ reflect.Type) (callbacks, subscriptions) {
callbacks := make(callbacks)
subscriptions := make(subscriptions)
METHODS:
for m := 0; m < typ.NumMethod(); m++ {
method := typ.Method(m)
mtype := method.Type
//转小写
mname := formatName(method.Name)
if method.PkgPath != "" { // method must be exported
continue
var h callback
//订阅事件类型判断 主要根据签名的入参第二位和返回参数第一位
h.isSubscribe = isPubSub(mtype)
h.rcvr = rcvr
h.method = method
h.errPos = -1
firstArg := 1
numIn := mtype.NumIn()
if numIn >= 2 && mtype.In(1) == contextType {
h.hasCtx = true
firstArg = 2
if h.isSubscribe {
//订阅类型
h.argTypes = make([]reflect.Type, numIn-firstArg) // skip rcvr type
for i := firstArg; i < numIn; i++ {
argType := mtype.In(i)
if isExportedOrBuiltinType(argType) {
h.argTypes[i-firstArg] = argType
} else {
continue METHODS
subscriptions[mname] = &h
continue METHODS
// determine method arguments, ignore first arg since it's the receiver type
// Arguments must be exported or builtin types
h.argTypes = make([]reflect.Type, numIn-firstArg)
for i := firstArg; i < numIn; i++ {
argType := mtype.In(i)
if !isExportedOrBuiltinType(argType) {
continue METHODS
h.argTypes[i-firstArg] = argType
// check that all returned values are exported or builtin types
for i := 0; i < mtype.NumOut(); i++ {
if !isExportedOrBuiltinType(mtype.Out(i)) {
continue METHODS
// when a method returns an error it must be the last returned value
h.errPos = -1
for i := 0; i < mtype.NumOut(); i++ {
if isErrorType(mtype.Out(i)) {
h.errPos = i
break
if h.errPos >= 0 && h.errPos != mtype.NumOut()-1 {
continue METHODS
switch mtype.NumOut() {
case 0, 1, 2:
if mtype.NumOut() == 2 && h.errPos == -1 { // method must one return value and 1 error
continue METHODS
callbacks[mname] = &h
return callbacks, subscriptions
### 2.2.2 底层协议
底层支持了InProc,IPC,HTTP,WEBSOCKED 四种传输协议
* 1 InProc 直接生成RPCService实例,挂在Node上面可以直接调用。
* 2 IPC 监听管道,收到消息后解析成ServerCodec对象,扔给Server的ServeCodec方法使用;
//file ipc.go
func (srv *Server) ServeListener(l net.Listener) error {
for {
conn, err := l.Accept()
if netutil.IsTemporaryError(err) {
log.Warn("RPC accept error", "err", err)
continue
} else if err != nil {
return err
log.Trace("Accepted connection", "addr", conn.RemoteAddr())
go srv.ServeCodec(NewJSONCodec(conn), OptionMethodInvocation|OptionSubscriptions)
* 3 HTTP 生成两个中间件,第二个中间件接收消息生成ServerCOdec,扔给Server的ServeSingleRequest方法
//file http.go
func (srv *Server) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Permit dumb empty requests for remote health-checks (AWS)
if r.Method == http.MethodGet && r.ContentLength == 0 && r.URL.RawQuery == "" {
return
if code, err := validateRequest(r); err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), code)
return
// All checks passed, create a codec that reads direct from the request body
// untilEOF and writes the response to w and order the server to process a
// single request.
ctx := context.Background()
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "remote", r.RemoteAddr)
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "scheme", r.Proto)
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "local", r.Host)
body := io.LimitReader(r.Body, maxRequestContentLength)
codec := NewJSONCodec(&httpReadWriteNopCloser{body, w})
defer codec.Close()
w.Header().Set("content-type", contentType)
srv.ServeSingleRequest(codec, OptionMethodInvocation, ctx)
* 1 WEBSOCKED 与Http类型生成WebsocketHandler中间件,到消息后解析成ServerCodec对象,扔给Server的ServeCodec方法使用
//websocked.go
func (srv *Server) WebsocketHandler(allowedOrigins []string) http.Handler {
return websocket.Server{
Handshake: wsHandshakeValidator(allowedOrigins),
Handler: func(conn *websocket.Conn) {
// Create a custom encode/decode pair to enforce payload size and number encoding
conn.MaxPayloadBytes = maxRequestContentLength
encoder := func(v interface{}) error {
return websocketJSONCodec.Send(conn, v)
decoder := func(v interface{}) error {
return websocketJSONCodec.Receive(conn, v)
srv.ServeCodec(NewCodec(conn, encoder, decoder), OptionMethodInvocation|OptionSubscriptions)
### 2.2.3 rpc响应
上面四种协议再拿到ServerCodec对象后,会把这个对象传递到service的响应请数里面去。最终都是调到handle函数里面,handle里面再根据不同的类型进行响应。
func (s *Server) handle(ctx context.Context, codec ServerCodec, req *serverRequest) (interface{}, func()) {
if req.err != nil {
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, req.err), nil
if req.isUnsubscribe {
//取消订阅功能
if len(req.args) >= 1 && req.args[0].Kind() == reflect.String {
notifier, supported := NotifierFromContext(ctx) //获取notifier对象
if !supported { // interface doesn't support subscriptions (e.g. http)
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{ErrNotificationsUnsupported.Error()}), nil
//取消订阅
subid := ID(req.args[0].String())
if err := notifier.unsubscribe(subid); err != nil {
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{err.Error()}), nil
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, true), nil
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &invalidParamsError{"Expected subscription id as first argument"}), nil
if req.callb.isSubscribe {
//订阅功能
subid, err := s.createSubscription(ctx, codec, req)
if err != nil {
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{err.Error()}), nil
// active the subscription after the sub id was successfully sent to the client
activateSub := func() {
notifier, _ := NotifierFromContext(ctx) //获取notifier对象
notifier.activate(subid, req.svcname) //订阅事件
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, subid), activateSub
// regular RPC call, prepare arguments
//参数生成
if len(req.args) != len(req.callb.argTypes) {
rpcErr := &invalidParamsError{fmt.Sprintf("%s%s%s expects %d parameters, got %d",
req.svcname, serviceMethodSeparator, req.callb.method.Name,
len(req.callb.argTypes), len(req.args))}
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, rpcErr), nil
arguments := []reflect.Value{req.callb.rcvr}
if req.callb.hasCtx {
arguments = append(arguments, reflect.ValueOf(ctx))
if len(req.args) > 0 {
arguments = append(arguments, req.args...)
// execute RPC method and return result
//执行对应的函数
reply := req.callb.method.Func.Call(arguments)
if len(reply) == 0 {
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, nil), nil
//校验结果
if req.callb.errPos >= 0 { // test if method returned an error
if !reply[req.callb.errPos].IsNil() {
e := reply[req.callb.errPos].Interface().(error)
res := codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{e.Error()})
return res, nil
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, reply[0].Interface()), nil
### 2.2.4 Pub/sub 实现
底层在context绑定一个notifier对象
if options&OptionSubscriptions == OptionSubscriptions {
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, notifierKey{}, newNotifier(codec))
sub/unsub的时候会通过context.Value中拿notifier对象,调用上面的方法
##### 注册或者取消注册
func NotifierFromContext(ctx context.Context) (*Notifier, bool) {
n, ok := ctx.Value(notifierKey{}).(*Notifier)
return n, ok
##### 注册
func (n *Notifier) activate(id ID, namespace string) {
n.subMu.Lock()
defer n.subMu.Unlock()
if sub, found := n.inactive[id]; found {
sub.namespace = namespace
n.active[id] = sub
delete(n.inactive, id)
##### 注销
func (n *Notifier) unsubscribe(id ID) error {
n.subMu.Lock()
defer n.subMu.Unlock()
if s, found := n.active[id]; found {
close(s.err)
delete(n.active, id)
return nil
return ErrSubscriptionNotFound
##### 消息事件触发
func (api *PrivateAdminAPI) PeerEvents(ctx context.Context) (*rpc.Subscription, error) {
// Make sure the server is running, fail otherwise
server := api.node.Server()
if server == nil {
return nil, ErrNodeStopped
// Create the subscription
//获取notifier对象
notifier, supported := rpc.NotifierFromContext(ctx)
if !supported {
return nil, rpc.ErrNotificationsUnsupported
//生成标识
rpcSub := notifier.CreateSubscription()
go func() {
events := make(chan *p2p.PeerEvent)
sub := server.SubscribeEvents(events)
defer sub.Unsubscribe()
for {
select {
case event := <-events:
//触发事件,发送通知消息
notifier.Notify(rpcSub.ID, event)
case <-sub.Err():
return
case <-rpcSub.Err():
return
case <-notifier.Closed():
return
return rpcSub, nil
## 2.2.5 rpc client调用
以太坊提供了RPC服务,可以在geth启动时通过参数设置
### 2.2.5.1 geth启动选项参数
--rpc 启动HTTP-RPC服务(基于HTTP的)
--ws 启动WS-RPC服务(基于WebService的)
--rpcapi value 指定需要调用的HTTP-RPC API接口,默认只有eth,net,web3
--rpcport value HTTP-RPC服务器监听端口(default: 8545)
--rpcport value HTTP-RPC服务器监听端口(default: 8545)
例子:geth --rpc --rpcapi "db,eth,net,web3,personal"
执行RPC调用的方式有很多,可以使用web3提供的接口、直接发送Json请求(缺点是拼json会很麻烦)、使用go-ethereum/ethclient包提供的函数(缺点是只有eth接口)、也可以自己定义接口来调用。下面代码是使用go-ethereum/ethclient包中的函数的例子。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/mobile"
func main() {
// NewEthereumClient函数只是创建一个EthereumClient结构,并设置了HTTP连接的一些参数如的head的一些属性,并没有节点建立连接
cli, err := geth.NewEthereumClient("http://127.0.0.1:8545")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("create new ethereum rpc client err:%s\n", err.Error())
} else {
fmt.Println("create new ethereum rpc client success")
eth_ctx := geth.NewContext()
block, err2 := cli.GetBlockByNumber(eth_ctx, 18)
fmt.Printf("ethereum mobile Context:%+v\n", eth_ctx)
if err2 != nil {
fmt.Printf("get block err:%s\n", err2.Error())
} else {
fmt.Printf("block:%+v\n", block)
连的节点是本地运行的私有链,并且在go-ethereum源码中加了一些日志,执行结果:
mylog:DialContext:u:{Scheme:http Opaque: User: Host:127.0.0.1:8545 Path: RawPath: ForceQuery:false RawQuery: Fragment:};
mylog:u.Scheme:http
create new ethereum rpc client success
mylog:JSON-RPC: Client CallContext
mylog:Client.isHTTP:true
ethereum mobile Context:&{context:0xc4200ac008 cancel:
}
block:Block(#18): Size: 650.00 B {
MinerHash: fd55c05ae10a5b0159b3c2d5803c6aa9469c95f5f063b9c400a2c36b49616ab3
Header(84b2cfd65e3197bdfe3f748ecebb040953af5eb73a05d8595757cf42cb40a492):
ParentHash: 7892a0b31d50d67ae20d4a7ec5c24a6fe85f2f264e9f1639aa2388081305a0bd
UncleHash: 1dcc4de8dec75d7aab85b567b6ccd41ad312451b948a7413f0a142fd40d49347
Coinbase: bdc61c81f67983288a6c375a884661edc77286d0
Root: 0f30637bfc5bd6e123c6a0c38bdc743c94050626a984f9943eaf38367100b3e3
TxSha 354d185cfa88e50f1a425e5b89500122e4445e9ec737e7a18cdd61b9350ab72b
ReceiptSha: a769d28981014fb6095462148a6300cd0b43fa050d75eb6f5b7595cfd13136bb
Bloom: 00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Difficulty: 131072
Number: 18
GasLimit: 131877941
GasUsed: 21000
Time: 1527044372
Extra: ׃��geth�go1.10�darwin
MixDigest: 70c2bb422b1b834d5173d279e508ffee9dada454650fc3cf63e95deb3073cf32
Nonce: 58b7495f112ccac2
Transactions:
TX(57a3b17f84358098b728fc0f70f0697f175f8ba00d386c88eac0815b3afd6aad)
Contract: false
From: 2154bdd7070c99d1a25ff589a08b01dfd6eb65de
To: bdc61c81f67983288a6c375a884661edc77286d0
Nonce: 0
GasPrice: 0x430e23400
GasLimit 0x15f90
Value: 0xde0b6b3a7640000
Data: 0x
V: 0x41
R: 0x45d4952c0190373c56e62ad15e54db54c0246385371b23c70bab4126b51927f8
S: 0x618e4bb76a36482254352d7e5096c0dff4c1f495218d57c874fc3d8153915ea4
Hex: f86d80850430e2340083015f9094bdc61c81f67983288a6c375a884661edc77286d0880de0b6b3a76400008041a045d4952c0190373c56e62ad15e54db54c0246385371b23c70bab4126b51927f8a0618e4bb76a36482254352d7e5096c0dff4c1f495218d57c874fc3d8153915ea4
Uncles:
### 2.2.5.2 分析:
**go-ethereum/mobile包** 是发起RPC请求的客户端直接使用的包。
该包中有 `EthereumClient` 结构提供了Ethereum API的接入。
// EthereumClient provides access to the Ethereum APIs.
type EthereumClient struct {
client *ethclient.Client
ethclient.Client在ethclient包中,包装了rpc.Client,rpc.Client代表与RPC服务的一个连接。
// Client defines typed wrappers for the Ethereum RPC API.
type Client struct {
c *rpc.Client
RPC请求客户端在使用时,首先传入想要接入的节点的url作为参数,调用mobile包中的NewEthereumClient函数。创建了EthereumClient实例,并与节点建立连接。建立的RPC连接有三种形式:HTTP、WebSocket、IPC,当传入 `http://127.0.0.1:8545` 时,建立的是HTTP连接。
// NewEthereumClient connects a client to the given URL.
func NewEthereumClient(rawurl string) (client *EthereumClient, _ error) {
rawClient, err := ethclient.Dial(rawurl)
return &EthereumClient{rawClient}, err
设置HTTP连接的参数会调用rpc包http.go文件中的DialHTTPWithClient函数。
// DialHTTPWithClient creates a new RPC client that connects to an RPC server over HTTP
// using the provided HTTP Client.
func DialHTTPWithClient(endpoint string, client *http.Client) (*Client, error) {
req, err := http.NewRequest(http.MethodPost, endpoint, nil)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
// Content-Type和Accept是application/json,即发送的数据类型和接收的数据类型都是json
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", contentType)
req.Header.Set("Accept", contentType)
initctx := context.Background()
return newClient(initctx, func(context.Context) (net.Conn, error) {
return &httpConn{client: client, req: req, closed: make(chan struct{})}, nil
通过HTTP来做JSON-RPC调用时,需要一个geth.Context实例,通过调用mobile包中的NewContext函数,创建一个空的geth.Context实例。
// NewContext returns a non-nil, empty Context. It is never canceled, has no
// values, and has no deadline. It is typically used by the main function,
// initialization, and tests, and as the top-level Context for incoming requests.
func NewContext() *Context {
return &Context{
context: context.Background(),
mobile包中封装了请求区块、区块头、交易等函数,这些函数调用ethclient包中的相关函数,再调用更底层rpc包中封装的函数。
即 **mobile包-->ethclient包-->rpc包** 。如mobile包中根据区块号查找区块的函数最后会调用rpc包中的CallContext函数。
// CallContext扮演JSON-RPC调用角色
// CallContext performs a JSON-RPC call with the given arguments. If the context is
// canceled before the call has successfully returned, CallContext returns immediately.
// The result must be a pointer so that package json can unmarshal into it. You
// can also pass nil, in which case the result is ignored.
func (c *Client) CallContext(ctx context.Context, result interface{}, method string, args ...interface{}) error {
fmt.Printf("mylog:JSON-RPC: Client CallContext\n")
msg, err := c.newMessage(method, args...)
if err != nil {
return err
op := &requestOp{ids: []json.RawMessage{msg.ID}, resp: make(chan *jsonrpcMessage, 1)}
fmt.Printf("mylog:Client.isHTTP:%+v\n",c.isHTTP)
if c.isHTTP {
err = c.sendHTTP(ctx, op, msg)
} else {
err = c.send(ctx, op, msg)
if err != nil {
return err
// dispatch has accepted the request and will close the channel it when it quits.
switch resp, err := op.wait(ctx); {
case err != nil:
return err
case resp.Error != nil:
return resp.Error
case len(resp.Result) == 0:
return ErrNoResult
default:
return json.Unmarshal(resp.Result, &result)
### 2.2.5.3 使用POSTMAN
使用POSTMAN发送请求时,注意设置下Content-type和Accept。
body是 `{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"web3_clientVersion","params":[],"id":67}`
这种方式虽然直接,但是自己拼json会很麻烦,所以最方便的还是调用已有的接口。
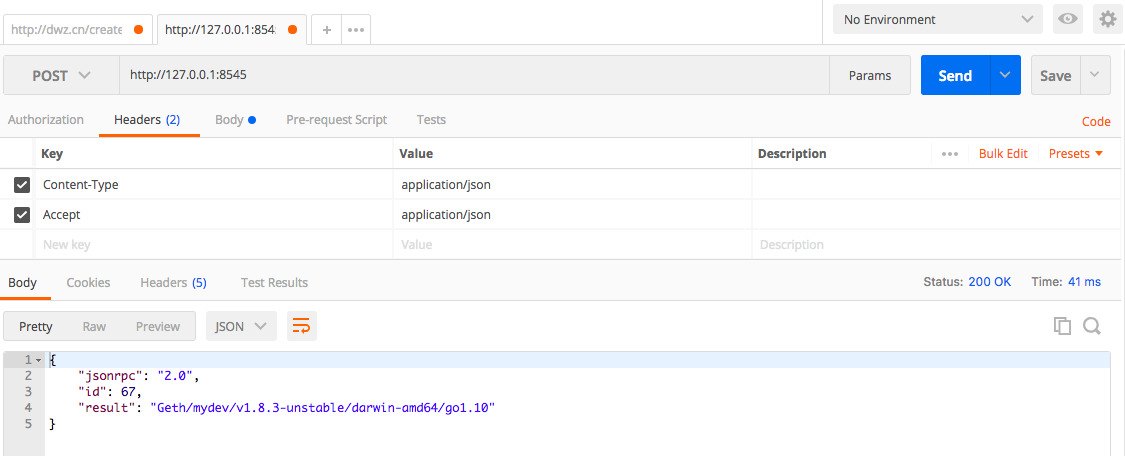
如果是做查询区块号为18的区块,则body是
`{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"eth_getBlockByNumber","params":["0x12",true],"id":1}`
# 3\. 参考
(1)以太坊源码深入分析(3)-- 以太坊RPC通信实例和原理代码分析(上)
[https://www.jianshu.com/p/92daf6148dc5](https://www.jianshu.com/p/92daf6148dc5)
(2)以太坊RPC
[https://www.jianshu.com/p/8bd3723aa921](https://www.jianshu.com/p/8bd3723aa921)
(3)以太坊RPC原理及实现
[https://my.oschina.net/hunjixin/blog/1803161](https://my.oschina.net/hunjixin/blog/1803161)
(4)从零开始实现RPC框架 - RPC原理及实现
[https://www.jianshu.com/p/dbfac2b876b1](https://www.jianshu.com/p/dbfac2b876b1)
(5)深入浅出RPC原理
[https://ketao1989.github.io/2016/12/10/rpc-theory-in-action/](https://ketao1989.github.io/2016/12/10/rpc-theory-in-action/)
(6)你应该知道的RPC原理
[https://www.cnblogs.com/LBSer/p/4853234.html](https://www.cnblogs.com/LBSer/p/4853234.html)
(7)RPC原理解析
[https://www.cnblogs.com/swordfall/p/8683905.html](https://www.cnblogs.com/swordfall/p/8683905.html)
(8)服务之间的调用之RPC、Restful深入理解
[https://blog.csdn.net/u014590757/article/details/80233901](https://blog.csdn.net/u014590757/article/details/80233901)
本文介绍RPC协议的原理和调用流程,同时介绍以太坊RPC的实现机制。
2. 内容
2.1 RPC协议和调用流程
2.1.1 远程过程调用 (RPC)
Remote Procedure Calls 远程过程调用 (RPC) 是一种协议,就是从一台机器(客户端)上通过参数传递的方式调用另一台机器(服务器)上的一个函数或方法(可以统称为服务)并得到返回的结果。
通常的实现有
XML-RPC , JSON-RPC ,
通信方式基本相同, 所不同的只是传输数据的格式。
RPC是分布式架构的核心,按响应方式分如下两种:
同步调用:
客户端调用服务方方法,等待直到服务方返回结果或者超时,再继续自己的操作;
异步调用:
客户端把消息发送给中间件,不再等待服务端返回,直接继续自己的操作;
同步调用的实现方式有WebService和RMI。
Web Service提供的服务是基于web容器的,底层使用http协议,因而适合不同语言异构系统间的调用。
RMI(Remote Method Invocation,远程方法调用)实际上是Java语言的RPC实现,允许方法返回 Java 对象以及基本数据类型,适合用于JAVA语言构建的不同系统间的调用。
异步调用的JAVA实现版就是JMS(Java Message Service),目前开源的的JMS中间件有Apache社区的ActiveMQ、Kafka消息中间件,另外有阿里的RocketMQ。
2.1.2 RPC框架
一个完整的RPC架构里面包含了四个核心的组件,分别是Client,Client Stub,Server以及Server Stub,这个Stub可以理解为存根。
客户端(Client),服务的调用方。
客户端存根(Client Stub),存放服务端的地址消息,再将客户端的请求参数打包成网络消息,然后通过网络远程发送给服务方。
服务端(Server),真正的服务提供者。
服务端存根(Server Stub),接收客户端发送过来的消息,将消息解包,并调用本地的方法。
2.1.3 RPC调用流程
具体实现步骤:
1、 服务调用方(client)(客户端)以本地调用方式调用服务;
2、 client stub接收到调用后负责将方法、参数等组装成能够进行网络传输的消息体;在Java里就是序列化的过程;
3、 client stub找到服务地址,并将消息通过网络发送到服务端;
4、 server stub收到消息后进行解码,在Java里就是反序列化的过程;
5、 server stub根据解码结果调用本地的服务;
6、 本地服务执行处理逻辑;
7、 本地服务将结果返回给server stub;
8、 server stub将返回结果打包成消息,Java里的序列化;
9、 server stub将打包后的消息通过网络并发送至消费方;
10、 client stub接收到消息,并进行解码, Java里的反序列化;
11、 服务调用方(client)得到最终结果。
RPC框架的目标就是把2-10步封装起来,把调用、编码/解码的过程封装起来,让用户像调用本地服务一样的调用远程服务。要做到对客户端(调用方)透明化服务, RPC框架需要考虑解决如下问题:
1、通讯问题
: 主要是通过在客户端和服务器之间建立TCP连接,远程过程调用的所有交换的数据都在这个连接里传输。连接可以是按需连接,调用结束后就断掉,也可以是长连接,多个远程过程调用共享同一个连接。
2、寻址问题
: A服务器上的应用怎么告诉底层的RPC框架,如何连接到B服务器(如主机或IP地址)以及特定的端口,方法的名称是什么,这样才能完成调用。比如基于Web服务协议栈的RPC,就要提供一个endpoint URI,或者是从UDDI服务上查找。如果是RMI调用的话,还需要一个RMI Registry来注册服务的地址。
3、序列化与反序列化
: 当A服务器上的应用发起远程过程调用时,方法的参数需要通过底层的网络协议如TCP传递到B服务器,由于网络协议是基于二进制的,内存中的参数的值要序列化成二进制的形式,也就是序列化(Serialize)或编组(marshal),通过寻址和传输将序列化的二进制发送给B服务器。
同理,B服务器接收参数要将参数反序列化。B服务器应用调用自己的方法处理后返回的结果也要序列化给A服务器,A服务器接收也要经过反序列化的过程。
2.2 以太坊RPC实现
JSON-RPC是区块链外部调用的标配了。以太坊同样也实现了这个功能。底层支持四种协议:InProc,IPC,HTTP,WEBSOCKED。上层除了常规的方法调用之外还实现了Pub/Sub功能。本文主要分析以太坊是如何支持这些个功能的。
2.2.1 api发布
api接口分布在各个模块,主要分为两种
1:直接code在Node中的几个service(admin,web3j,debug etc)
2: 实现了Service接口的服务结构,已经注册的服务会调用APIs()方法获得其中的api。
//file go-ethereum/node/node.go
func (n *Node) startRPC(services map[reflect.Type]Service) error {
apis := n.apis()
for _, service := range services {
apis = append(apis, service.APIs()...)
node中写死的接口
// node中写死的接口
func (n *Node) apis() []rpc.API {
return []rpc.API{
Namespace: "admin",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateAdminAPI(n),
Namespace: "admin",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicAdminAPI(n),
Public: true,
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: debug.Handler,
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicDebugAPI(n),
Public: true,
Namespace: "web3",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicWeb3API(n),
Public: true,
Ethereum 服务实现的APIs()接口 类似的还有其他的服务(dashboard,ethstats)
//Ethereum 服务实现的APIs()接口
func (s *Ethereum) APIs() []rpc.API {
apis := ethapi.GetAPIs(s.ApiBackend)
// Append any APIs exposed explicitly by the consensus engine
apis = append(apis, s.engine.APIs(s.BlockChain())...)
// Append all the local APIs and return
return append(apis, []rpc.API{
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicEthereumAPI(s),
Public: true,
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicMinerAPI(s),
Public: true,
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: downloader.NewPublicDownloaderAPI(s.protocolManager.downloader, s.eventMux),
Public: true,
Namespace: "miner",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateMinerAPI(s),
Public: false,
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: filters.NewPublicFilterAPI(s.ApiBackend, false),
Public: true,
Namespace: "admin",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateAdminAPI(s),
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicDebugAPI(s),
Public: true,
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateDebugAPI(s.chainConfig, s),
Namespace: "net",
Version: "1.0",
Service: s.netRPCService,
Public: true,
}...)
这里的Service只是类型,还要注册到Server里面,原理就是反射出结构体里的类型,解析出函数方法名称(转小写),参数名称,返回类型等信息,最终每个合格的方法都会生成service实例。
type service struct {
name string // name for service
typ reflect.Type // receiver type
callbacks callbacks // registered handlers
subscriptions subscriptions // available subscriptions/notifications
//反射除Service Api的结构方法
//file go-ethereum/rpc/utils.go
func suitableCallbacks(rcvr reflect.Value, typ reflect.Type) (callbacks, subscriptions) {
callbacks := make(callbacks)
subscriptions := make(subscriptions)
METHODS:
for m := 0; m < typ.NumMethod(); m++ {
method := typ.Method(m)
mtype := method.Type
//转小写
mname := formatName(method.Name)
if method.PkgPath != "" { // method must be exported
continue
var h callback
//订阅事件类型判断 主要根据签名的入参第二位和返回参数第一位
h.isSubscribe = isPubSub(mtype)
h.rcvr = rcvr
h.method = method
h.errPos = -1
firstArg := 1
numIn := mtype.NumIn()
if numIn >= 2 && mtype.In(1) == contextType {
h.hasCtx = true
firstArg = 2
if h.isSubscribe {
//订阅类型
h.argTypes = make([]reflect.Type, numIn-firstArg) // skip rcvr type
for i := firstArg; i < numIn; i++ {
argType := mtype.In(i)
if isExportedOrBuiltinType(argType) {
h.argTypes[i-firstArg] = argType
} else {
continue METHODS
subscriptions[mname] = &h
continue METHODS
// determine method arguments, ignore first arg since it's the receiver type
// Arguments must be exported or builtin types
h.argTypes = make([]reflect.Type, numIn-firstArg)
for i := firstArg; i < numIn; i++ {
argType := mtype.In(i)
if !isExportedOrBuiltinType(argType) {
continue METHODS
h.argTypes[i-firstArg] = argType
// check that all returned values are exported or builtin types
for i := 0; i < mtype.NumOut(); i++ {
if !isExportedOrBuiltinType(mtype.Out(i)) {
continue METHODS
// when a method returns an error it must be the last returned value
h.errPos = -1
for i := 0; i < mtype.NumOut(); i++ {
if isErrorType(mtype.Out(i)) {
h.errPos = i
break
if h.errPos >= 0 && h.errPos != mtype.NumOut()-1 {
continue METHODS
switch mtype.NumOut() {
case 0, 1, 2:
if mtype.NumOut() == 2 && h.errPos == -1 { // method must one return value and 1 error
continue METHODS
callbacks[mname] = &h
return callbacks, subscriptions
2.2.2 底层协议
底层支持了InProc,IPC,HTTP,WEBSOCKED 四种传输协议
1 InProc 直接生成RPCService实例,挂在Node上面可以直接调用。
2 IPC 监听管道,收到消息后解析成ServerCodec对象,扔给Server的ServeCodec方法使用;
//file ipc.go
func (srv *Server) ServeListener(l net.Listener) error {
for {
conn, err := l.Accept()
if netutil.IsTemporaryError(err) {
log.Warn("RPC accept error", "err", err)
continue
} else if err != nil {
return err
log.Trace("Accepted connection", "addr", conn.RemoteAddr())
go srv.ServeCodec(NewJSONCodec(conn), OptionMethodInvocation|OptionSubscriptions)
3 HTTP 生成两个中间件,第二个中间件接收消息生成ServerCOdec,扔给Server的ServeSingleRequest方法
//file http.go
func (srv *Server) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Permit dumb empty requests for remote health-checks (AWS)
if r.Method == http.MethodGet && r.ContentLength == 0 && r.URL.RawQuery == "" {
return
if code, err := validateRequest(r); err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), code)
return
// All checks passed, create a codec that reads direct from the request body
// untilEOF and writes the response to w and order the server to process a
// single request.
ctx := context.Background()
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "remote", r.RemoteAddr)
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "scheme", r.Proto)
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "local", r.Host)
body := io.LimitReader(r.Body, maxRequestContentLength)
codec := NewJSONCodec(&httpReadWriteNopCloser{body, w})
defer codec.Close()
w.Header().Set("content-type", contentType)
srv.ServeSingleRequest(codec, OptionMethodInvocation, ctx)
1 WEBSOCKED 与Http类型生成WebsocketHandler中间件,到消息后解析成ServerCodec对象,扔给Server的ServeCodec方法使用
//websocked.go
func (srv *Server) WebsocketHandler(allowedOrigins []string) http.Handler {
return websocket.Server{
Handshake: wsHandshakeValidator(allowedOrigins),
Handler: func(conn *websocket.Conn) {
// Create a custom encode/decode pair to enforce payload size and number encoding
conn.MaxPayloadBytes = maxRequestContentLength
encoder := func(v interface{}) error {
return websocketJSONCodec.Send(conn, v)
decoder := func(v interface{}) error {
return websocketJSONCodec.Receive(conn, v)
srv.ServeCodec(NewCodec(conn, encoder, decoder), OptionMethodInvocation|OptionSubscriptions)
2.2.3 rpc响应
上面四种协议再拿到ServerCodec对象后,会把这个对象传递到service的响应请数里面去。最终都是调到handle函数里面,handle里面再根据不同的类型进行响应。
func (s *Server) handle(ctx context.Context, codec ServerCodec, req *serverRequest) (interface{}, func()) {
if req.err != nil {
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, req.err), nil
if req.isUnsubscribe {
//取消订阅功能
if len(req.args) >= 1 && req.args[0].Kind() == reflect.String {
notifier, supported := NotifierFromContext(ctx) //获取notifier对象
if !supported { // interface doesn't support subscriptions (e.g. http)
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{ErrNotificationsUnsupported.Error()}), nil
//取消订阅
subid := ID(req.args[0].String())
if err := notifier.unsubscribe(subid); err != nil {
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{err.Error()}), nil
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, true), nil
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &invalidParamsError{"Expected subscription id as first argument"}), nil
if req.callb.isSubscribe {
//订阅功能
subid, err := s.createSubscription(ctx, codec, req)
if err != nil {
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{err.Error()}), nil
// active the subscription after the sub id was successfully sent to the client
activateSub := func() {
notifier, _ := NotifierFromContext(ctx) //获取notifier对象
notifier.activate(subid, req.svcname) //订阅事件
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, subid), activateSub
// regular RPC call, prepare arguments
//参数生成
if len(req.args) != len(req.callb.argTypes) {
rpcErr := &invalidParamsError{fmt.Sprintf("%s%s%s expects %d parameters, got %d",
req.svcname, serviceMethodSeparator, req.callb.method.Name,
len(req.callb.argTypes), len(req.args))}
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, rpcErr), nil
arguments := []reflect.Value{req.callb.rcvr}
if req.callb.hasCtx {
arguments = append(arguments, reflect.ValueOf(ctx))
if len(req.args) > 0 {
arguments = append(arguments, req.args...)
// execute RPC method and return result
//执行对应的函数
reply := req.callb.method.Func.Call(arguments)
if len(reply) == 0 {
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, nil), nil
//校验结果
if req.callb.errPos >= 0 { // test if method returned an error
if !reply[req.callb.errPos].IsNil() {
e := reply[req.callb.errPos].Interface().(error)
res := codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{e.Error()})
return res, nil
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, reply[0].Interface()), nil
2.2.4 Pub/sub 实现
底层在context绑定一个notifier对象
if options&OptionSubscriptions == OptionSubscriptions {
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, notifierKey{}, newNotifier(codec))
sub/unsub的时候会通过context.Value中拿notifier对象,调用上面的方法
注册或者取消注册
func NotifierFromContext(ctx context.Context) (*Notifier, bool) {
n, ok := ctx.Value(notifierKey{}).(*Notifier)
return n, ok
func (n *Notifier) activate(id ID, namespace string) {
n.subMu.Lock()
defer n.subMu.Unlock()
if sub, found := n.inactive[id]; found {
sub.namespace = namespace
n.active[id] = sub
delete(n.inactive, id)
func (n *Notifier) unsubscribe(id ID) error {
n.subMu.Lock()
defer n.subMu.Unlock()
if s, found := n.active[id]; found {
close(s.err)
delete(n.active, id)
return nil
return ErrSubscriptionNotFound
消息事件触发
func (api *PrivateAdminAPI) PeerEvents(ctx context.Context) (*rpc.Subscription, error) {
// Make sure the server is running, fail otherwise
server := api.node.Server()
if server == nil {
return nil, ErrNodeStopped
// Create the subscription
//获取notifier对象
notifier, supported := rpc.NotifierFromContext(ctx)
if !supported {
return nil, rpc.ErrNotificationsUnsupported
//生成标识
rpcSub := notifier.CreateSubscription()
go func() {
events := make(chan *p2p.PeerEvent)
sub := server.SubscribeEvents(events)
defer sub.Unsubscribe()
for {
select {
case event := <-events:
//触发事件,发送通知消息
notifier.Notify(rpcSub.ID, event)
case <-sub.Err():
return
case <-rpcSub.Err():
return
case <-notifier.Closed():
return
return rpcSub, nil
2.2.5 rpc client调用
以太坊提供了RPC服务,可以在geth启动时通过参数设置
2.2.5.1 geth启动选项参数
--rpc 启动HTTP-RPC服务(基于HTTP的)
--ws 启动WS-RPC服务(基于WebService的)
--rpcapi value 指定需要调用的HTTP-RPC API接口,默认只有eth,net,web3
--rpcport value HTTP-RPC服务器监听端口(default: 8545)
--rpcport value HTTP-RPC服务器监听端口(default: 8545)
例子:geth --rpc --rpcapi "db,eth,net,web3,personal"
执行RPC调用的方式有很多,可以使用web3提供的接口、直接发送Json请求(缺点是拼json会很麻烦)、使用go-ethereum/ethclient包提供的函数(缺点是只有eth接口)、也可以自己定义接口来调用。下面代码是使用go-ethereum/ethclient包中的函数的例子。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/mobile"
func main() {
// NewEthereumClient函数只是创建一个EthereumClient结构,并设置了HTTP连接的一些参数如的head的一些属性,并没有节点建立连接
cli, err := geth.NewEthereumClient("http://127.0.0.1:8545")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("create new ethereum rpc client err:%s\n", err.Error())
} else {
fmt.Println("create new ethereum rpc client success")
eth_ctx := geth.NewContext()
block, err2 := cli.GetBlockByNumber(eth_ctx, 18)
fmt.Printf("ethereum mobile Context:%+v\n", eth_ctx)
if err2 != nil {
fmt.Printf("get block err:%s\n", err2.Error())
} else {
fmt.Printf("block:%+v\n", block)
连的节点是本地运行的私有链,并且在go-ethereum源码中加了一些日志,执行结果:
mylog:DialContext:u:{Scheme:http Opaque: User: Host:127.0.0.1:8545 Path: RawPath: ForceQuery:false RawQuery: Fragment:};
mylog:u.Scheme:http
create new ethereum rpc client success
mylog:JSON-RPC: Client CallContext
mylog:Client.isHTTP:true
ethereum mobile Context:&{context:0xc4200ac008 cancel:<nil>}
block:Block(#18): Size: 650.00 B {
MinerHash: fd55c05ae10a5b0159b3c2d5803c6aa9469c95f5f063b9c400a2c36b49616ab3
Header(84b2cfd65e3197bdfe3f748ecebb040953af5eb73a05d8595757cf42cb40a492):
ParentHash: 7892a0b31d50d67ae20d4a7ec5c24a6fe85f2f264e9f1639aa2388081305a0bd
UncleHash: 1dcc4de8dec75d7aab85b567b6ccd41ad312451b948a7413f0a142fd40d49347
Coinbase: bdc61c81f67983288a6c375a884661edc77286d0
Root: 0f30637bfc5bd6e123c6a0c38bdc743c94050626a984f9943eaf38367100b3e3
TxSha 354d185cfa88e50f1a425e5b89500122e4445e9ec737e7a18cdd61b9350ab72b
ReceiptSha: a769d28981014fb6095462148a6300cd0b43fa050d75eb6f5b7595cfd13136bb
Bloom: 00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Difficulty: 131072
Number: 18
GasLimit: 131877941
GasUsed: 21000
Time: 1527044372
Extra: ׃��geth�go1.10�darwin
MixDigest: 70c2bb422b1b834d5173d279e508ffee9dada454650fc3cf63e95deb3073cf32
Nonce: 58b7495f112ccac2
Transactions:
TX(57a3b17f84358098b728fc0f70f0697f175f8ba00d386c88eac0815b3afd6aad)
Contract: false
From: 2154bdd7070c99d1a25ff589a08b01dfd6eb65de
To: bdc61c81f67983288a6c375a884661edc77286d0
Nonce: 0
GasPrice: 0x430e23400
GasLimit 0x15f90
Value: 0xde0b6b3a7640000
Data: 0x
V: 0x41
R: 0x45d4952c0190373c56e62ad15e54db54c0246385371b23c70bab4126b51927f8
S: 0x618e4bb76a36482254352d7e5096c0dff4c1f495218d57c874fc3d8153915ea4
Hex: f86d80850430e2340083015f9094bdc61c81f67983288a6c375a884661edc77286d0880de0b6b3a76400008041a045d4952c0190373c56e62ad15e54db54c0246385371b23c70bab4126b51927f8a0618e4bb76a36482254352d7e5096c0dff4c1f495218d57c874fc3d8153915ea4
Uncles:
2.2.5.2 分析:
go-ethereum/mobile包 是发起RPC请求的客户端直接使用的包。
该包中有 EthereumClient 结构提供了Ethereum API的接入。
// EthereumClient provides access to the Ethereum APIs.
type EthereumClient struct {
client *ethclient.Client
ethclient.Client在ethclient包中,包装了rpc.Client,rpc.Client代表与RPC服务的一个连接。
// Client defines typed wrappers for the Ethereum RPC API.
type Client struct {
c *rpc.Client
RPC请求客户端在使用时,首先传入想要接入的节点的url作为参数,调用mobile包中的NewEthereumClient函数。创建了EthereumClient实例,并与节点建立连接。建立的RPC连接有三种形式:HTTP、WebSocket、IPC,当传入 http://127.0.0.1:8545 时,建立的是HTTP连接。
// NewEthereumClient connects a client to the given URL.
func NewEthereumClient(rawurl string) (client *EthereumClient, _ error) {
rawClient, err := ethclient.Dial(rawurl)
return &EthereumClient{rawClient}, err
设置HTTP连接的参数会调用rpc包http.go文件中的DialHTTPWithClient函数。
// DialHTTPWithClient creates a new RPC client that connects to an RPC server over HTTP
// using the provided HTTP Client.
func DialHTTPWithClient(endpoint string, client *http.Client) (*Client, error) {
req, err := http.NewRequest(http.MethodPost, endpoint, nil)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
// Content-Type和Accept是application/json,即发送的数据类型和接收的数据类型都是json
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", contentType)
req.Header.Set("Accept", contentType)
initctx := context.Background()
return newClient(initctx, func(context.Context) (net.Conn, error) {
return &httpConn{client: client, req: req, closed: make(chan struct{})}, nil
通过HTTP来做JSON-RPC调用时,需要一个geth.Context实例,通过调用mobile包中的NewContext函数,创建一个空的geth.Context实例。
// NewContext returns a non-nil, empty Context. It is never canceled, has no
// values, and has no deadline. It is typically used by the main function,
// initialization, and tests, and as the top-level Context for incoming requests.
func NewContext() *Context {
return &Context{
context: context.Background(),
mobile包中封装了请求区块、区块头、交易等函数,这些函数调用ethclient包中的相关函数,再调用更底层rpc包中封装的函数。
即 mobile包-->ethclient包-->rpc包 。如mobile包中根据区块号查找区块的函数最后会调用rpc包中的CallContext函数。
// CallContext扮演JSON-RPC调用角色
// CallContext performs a JSON-RPC call with the given arguments. If the context is
// canceled before the call has successfully returned, CallContext returns immediately.
// The result must be a pointer so that package json can unmarshal into it. You
// can also pass nil, in which case the result is ignored.
func (c *Client) CallContext(ctx context.Context, result interface{}, method string, args ...interface{}) error {
fmt.Printf("mylog:JSON-RPC: Client CallContext\n")
msg, err := c.newMessage(method, args...)
if err != nil {
return err
op := &requestOp{ids: []json.RawMessage{msg.ID}, resp: make(chan *jsonrpcMessage, 1)}
fmt.Printf("mylog:Client.isHTTP:%+v\n",c.isHTTP)
if c.isHTTP {
err = c.sendHTTP(ctx, op, msg)
} else {
err = c.send(ctx, op, msg)
if err != nil {
return err
// dispatch has accepted the request and will close the channel it when it quits.
switch resp, err := op.wait(ctx); {
case err != nil:
return err
case resp.Error != nil:
return resp.Error
case len(resp.Result) == 0:
return ErrNoResult
default:
return json.Unmarshal(resp.Result, &result)
2.2.5.3 使用POSTMAN
使用POSTMAN发送请求时,注意设置下Content-type和Accept。
body是 {"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"web3_clientVersion","params":[],"id":67}
这种方式虽然直接,但是自己拼json会很麻烦,所以最方便的还是调用已有的接口。
如果是做查询区块号为18的区块,则body是
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"eth_getBlockByNumber","params":["0x12",true],"id":1}
3. 参考
(1)以太坊源码深入分析(3)-- 以太坊RPC通信实例和原理代码分析(上)
https://www.jianshu.com/p/92daf6148dc5
(2)以太坊RPC
https://www.jianshu.com/p/8bd3723aa921
(3)以太坊RPC原理及实现
https://my.oschina.net/hunjixin/blog/1803161
(4)从零开始实现RPC框架 - RPC原理及实现
https://www.jianshu.com/p/dbfac2b876b1
(5)深入浅出RPC原理
https://ketao1989.github.io/2016/12/10/rpc-theory-in-action/
(6)你应该知道的RPC原理
https://www.cnblogs.com/LBSer/p/4853234.html
(7)RPC原理解析
https://www.cnblogs.com/swordfall/p/8683905.html
(8)服务之间的调用之RPC、Restful深入理解
https://blog.csdn.net/u014590757/article/details/80233901